As with anything else, images come in different kinds and serve different purposes. Sometimes, a small size is important (for web sites) and at other times, retaining a high color depth (e.g., a family portrait) is what you want. GIMP can handle all of this, primarily by converting between three fundamental image modes, via → in the main menu. These three available modes are:
RGB: This is the default mode, used for high-quality images, and able to display millions of colors. This is also the mode for most of your image work including scaling, cropping, and even flipping. In RGB mode, each pixel consists of three different components: R->Red, G->Green, B->Blue. Each of these in turn can have an intensity value of 0-255. What you see at every pixel is an additive combination of these three components.
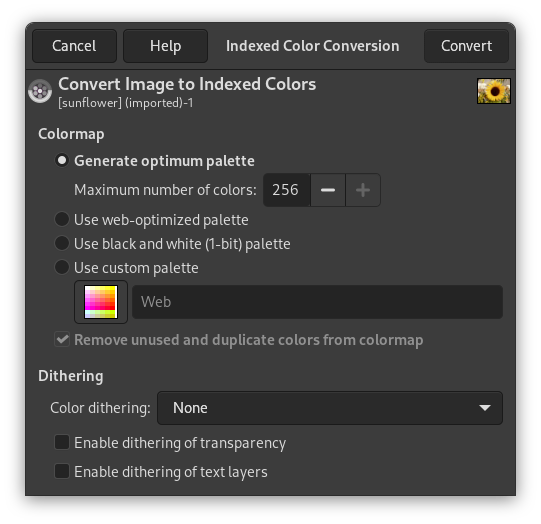
Indexed: This is the mode usually used when file size is of concern, or when you are working with images with few colors. It involves using a fixed number of colors (256 or less) for the entire image to represent colors. By default, when you change an image to a paletted image, GIMP generates an “optimum palette” to best represent your image.
As you might expect, since the information needed to represent the color at each pixel is less, the file size is smaller. However, sometimes, there are options in the various menus that are disabled for no apparent reason. This usually means that the filter or option cannot be applied when your image is in its current mode. Changing the mode to RGB, as outlined above, should solve this issue. If RGB mode doesn't work either, perhaps the option you're trying requires your layer to have the ability to be transparent. This can be done just as easily via → → .
Grayscale: Grayscale images have only shades of gray. This mode has some specific uses and takes less space on the hard drive in some formats, but is not recommended for general use as reading it is not supported by many applications.
Não há necessidade de converter uma imagem para um modo específico antes de exporta-la para seu formato favorito, já que o GIMP é inteligente o suficiente para exportar a imagem corretamente.