Ce filtre dessine des courbes Spirograph, épitrochoïdes et Lissajous. Une information immédiate est fournie, en dessinant dans un calque temporaire.
It reproduces curves drawn by Spirograph© toys. Here is an example from Wikimedia Commons showing what gears and holes are:

La roue mobile est à l’intérieur de la roue fixe et un trou est utilisé.
Much of the behavior of the plug-in is determined by options set outside of the plug-in, such as the current selection, or the settings of GIMP's tools. These settings can be changed while the plug-in is running.
![[Note]](images/note.png)
|
Note |
|---|---|
|
In contrast to options within the plug-in, changing the current selection or tool settings will not redraw the pattern. To show the changes, click the button at the bottom of the plug-in. |
As in most plug-ins, the current selection determines the area where the pattern will be rendered. Typically, this would be a rectangular selection. There is however, an additional way the selection can be used.
The selection can be used as the shape of the fixed gear (under the Fixed Gear tab). The plug-in will attempt to extract shapes from the selection, and draw a pattern inside of each shape. This is more interesting if you select a non-rectangular selection.
Pour que le motif embrasse les limites des formes, utilisez un pourcentage du trou = 100.
Spyrogimp uses GIMP's tools to perform the drawing. All the settings with which the drawings are done are taken from the chosen tool. For example, if you want to use the Pencil tool (by choosing it from the Tool menu), then all the settings of this tool will be used for drawing. You can change any of the tool settings while the plug-in is running, and press the button to see how the pattern looks.
La plupart des options sont organisées en trois onglets : Motif de courbe, Roue dentée fixe, et Taille.
- Type de courbe
-
The available curve types are: Spyrograph, Epitrochoid, Sine, and Lissajous. These correspond to physical models for drawing them, using either gears or springs. Spyrograph and Epitrochoid curves are obtained by using two gears - a fixed gear, and a moving gear. A Spyrograph pattern is obtained when the moving gear is rotated inside the fixed gear. When the moving gear is outside the fixed gear, an Epitrochoid pattern is generated. The Sine curve uses the fixed gear, but instead of a moving gear, there is a spring that moves perpendicular to the fixed gear's edge. The Lissajous curve is generated by two springs, which move on the x and y axis. It does not use the fixed ring at all, and thus is not affected by changing it.
Figure 17.412. Types de courbe « Spyrogimp »
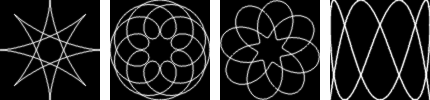
Types de courbe de gauche à droite : Spyrograph, Épitrochoïde, Sinus et Lissajous.
- Outil
-
The GIMP tool with which to draw the pattern. The first tool is named Preview and its purpose is to draw quickly, rather than beautifully - so the pattern can be previewed. The other available tools are: PaintBrush, Pencil, AirBrush, Stroke, Ink, and MyPaintBrush.
- Dégradé allongé
-
When unchecked, the current tool settings will be used - this can either produce a gradient or not, depending on the tool settings. When checked, the plug-in will produce a long gradient to match the length of the pattern, based on the current gradient, the "Reverse" setting, and the Repeat mode from the gradient tool settings. Setting the Repeat mode to Triangle Wave will produce a pattern that changes continuously, with no abrupt breaks. This is done by using the gradient followed by its reverse. Any other Repeat mode will simply use the gradient from start to finish.
Figure 17.413. Exemples de Dégradé allongé

The left image, without Long Gradient, used the paintbrush tool with a gradient. The two right images were generated with the same gradient, but with Long Gradient checked. The right image used the Triangle Wave Repeat mode.
Figure 17.414. Options du filtre « Spyrogimp »(Motif de courbe)
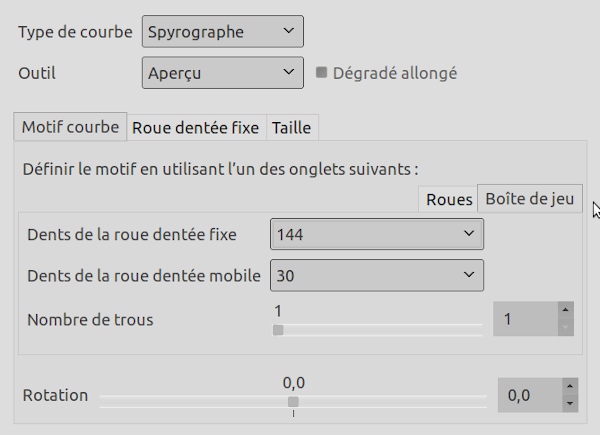
L’onglet Boîte de jeu est affiché à droite.
Specify a pattern using the Gears, Toy Kit or Visual tabs. The pattern is based only on the settings of the active tab. Toy Kit is similar to Gears, but it uses gears and hole numbers which are found in toy kits. If you follow the instructions from the toy kit manuals, you should obtain similar results.
- Dents de la roue dentée fixe
-
Nombre de dents de la roue dentée fixe. La taille des dents est proportionnelle au nombre de dents.
- Dents de la roue dentée mobile
-
Nombre de dents de la roue dentée mobile. La taille des dents est proportionnelle au nombre de dents.
- Pourcentage du trou
-
Distance entre le trou et le centre de la roue dentée mobile. 100% signifie que le trou est au bord de la roue dentée.
The Toy Kit tab also has Fixed Gear Teeth and Moving Gear Teeth options. In this case, however, they are limited to gear sizes that are provided with toy kits for drawing Spyrographs.
- Numéro de trous
-
Le trou n°1 est au bord de la roue dentée. Le numéro de trou maximal est proche du centre. Le numéro de trou maximal varie selon chaque roue dentée.
Figure 17.415. Exemples de « Boîte de jeu »
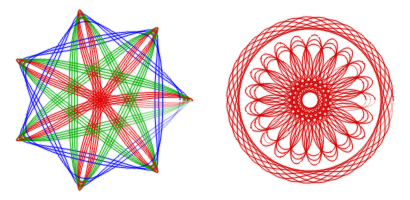
La Boîte jeu facilite la re-création de dessins de la boîte de jeu.L’image de gauche utilise une roue dentée fixe de 105, des roues dentées de 30 (bleue), 45 (verte) et 60 (rouge), où chaque roue dentée mobile a été utilise plusieurs fois avec un numéro de trou variant de 3 à 7. L’image de droite utilise aussi l’anneau de 105 fixe, avec un anneau mobile de 24 (trou n° 4), et un anneau mobile de 80 (trous n° 16, 18, 20).
Figure 17.416. Options du filtre « Spyrogimp »(Motif de courbe)
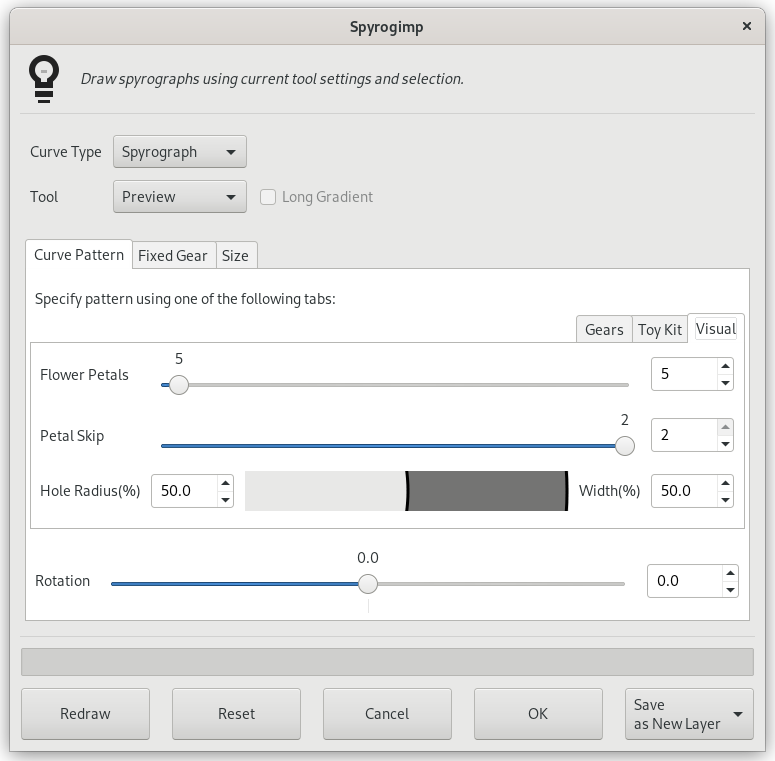
The Visual tab is shown in the middle on the right side.
The Visual tab creates more rounded, flower petal like patterns. It has the following settings:
- Flower Petals
-
The number of flower petals to draw.
- Petal Skip
-
The number of petals to skip.
- Hole radius (%)
-
The size of the hole.
- Width (%)
-
The width of the drawing.
Sous les onglets se trouve une autre otion.
- Rotation
-
Rotation du motif, en degrés. La position de départ de la roue dentée mobile est la roue dentée fixe. Notez que cela change aussi le motif lors du tracé de courbes Lissajous
- Forme
-
Forme de la roue dentée fixe à utiliser dans la sélection courante.
-
Cercle
-
Rack is a long round-edged shape provided in the toy kits.
-
Frame hugs the boundaries of the rectangular selection, use hole=100 in Gear notation to touch boundary. To generate a narrow frame width, use a small number of teeth for the moving gear.
-
Selection will hug boundaries of current selection - try something non-rectangular.
-
Polygon-Star morphs from an n-sided polygon (morph=0) to an n-sided star (morph=0.3) to a crazy flower (morph=1).
-
Sine with morph=0, it is just like a circle, but becomes more wavy as morph increases.
-
Bumps morphs from a polygon (morph=0) to a scalloped circle.
Figure 17.418. Exemples de formes « Spyrogimp »
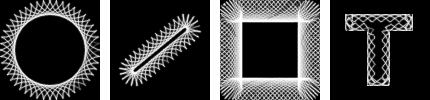
From left to right, Circle, Rack, Frame, and Selection shapes of the fixed gear. The selection in the right image was generated by selecting a large letter "T" that was produced by the text tool.
-
- Côtés
-
Number of sides of the shape.
This applies only to the Polygon-Star, Sine, and Bumps shapes. Otherwise this option is disabled.
- Morphing
-
Morph fixed gear shape.
This applies only to the Polygon-Star, Sine, and Bumps shapes. Otherwise this option is disabled.
- Rotation
-
Rotation de la roue fixe, en degrés.
- Marge (pixels)
-
Marge depuis le bord de la sélection. Contrôle la taille du motif.
- Rendre égales largeur et hauteur
-
Quand cette option n’est pas cochée, le motif remplit l’image ou la sélection courante. Quand elle est cochée, le motif a une largeur et une hauteur égales, et il est centré. La différence cochée/non-cochée n’est notable que si largeur et hauteur sont différentes.
- Enregistrer
-
The Save dropdown determines what will happen to the temporary layer once is pressed. Available options are: As New Layer, Redraw on last active layer, and As Path.
- Redessiner
-
If you change the settings of a tool, change color, or change the selection (i.e., any settings outside of the plug-in that affect the pattern), press this to update the preview to see how the pattern looks.
- Réinitialiser
-
Resets the dialog to its default settings.
- Annuler
-
Delete the temporary layer, and exit the plug-in.
- Valider
-
Render pattern to image.