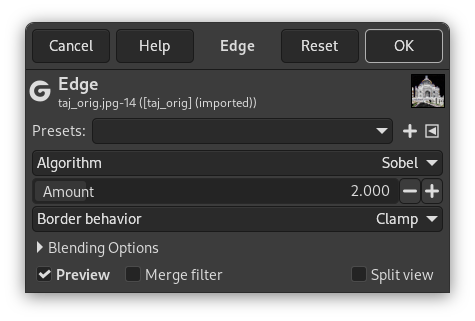
This filter detects edges in an image using the method selected in Algorithm.
- Presets, “Input Type”, Recortar, Blending Options, Vista previa, Merge filter, Split view
-
![[Nota]](images/note.png)
Nota Estas opciones se describen en la Sección 2, “Características comunes”.
- Algoritmo
-
The algorithm selected here, determines what method is used to detect edges. The following methods are available:
- Sobel
-
This is an alternative version of the separate Sobel filter. Contrary to that filter, this one has no additional settings that can be adjusted. This is the default; an example is shown at the top of the page.
- Prewitt
-
The Prewitt operator is a relatively fast algorithm, that can be relatively crude for high frequency variations in an image.

Algorithm set to Prewitt compass
- Degradado
-
When using the Gradient algoritm, edges are thinner, less contrasted and more blurred than Sobel.

Algorithm set to Gradient
- Roberts
-
The Roberts algorithm will highlight changes in intensity in a diagonal direction. However, it suffers greatly from sensitivity to noise.

Algorithm set to Roberts
- Diferencial
-
This algorithm often causes edges to be less bright.

Algorithm set to Differential
- Laplace
-
This is a different implementation of the Laplace filter, that gives different results.

Algorithm set to Laplace
- Cantidad
-
A low value results in a black, high-contrasted image with thin edges. A high value results in thick edges with low contrast and many colors in dark areas.
- Comportamiento en el borde
-
This determines where the edge detector will get adjoining pixels for its calculations when it is working on the image boundaries. This setting will only affect the boundaries of the result (if any). Clamp is the default and the best choice in general.