Αυτό το φίλτρο μετατοπίζει εικονοστοιχεία της ενεργής στρώσης ή επιλογής σύμφωνα με τις στάθμες του γκρι ενός χάρτη μετατόπισης. Τα εικονοστοιχεία μετατοπίζονται σύμφωνα με την κλίση διαβάθμισης στο χάρτη μετατόπισης. Τα εικονοστοιχεία που αντιστοιχούν στις συμπαγείς περιοχές δεν εμφανίζονται· όσο πιο μεγάλη η κλίση, τόσο μεγαλύτερη η μετατόπιση.
Σχήμα 17.330. Από αριστερά προς τα δεξιά: αρχική εικόνα, χάρτης μετατόπισης, μετατοπισμένη εικόνα

Οι συμπαγείς περιοχές του χάρτη μετατόπισης δεν οδηγούν σε μετατόπιση. Απότομες μεταβάσεις δίνουν μια σημαντική μετατόπιση. Μια γραμμική διαβάθμιση δίνει μια κανονική μετατόπιση. Η κατεύθυνση μετατόπισης είναι κάθετη στην κατεύθυνση διαβάθμισης (γωνία = 90°).
Σχήμα 17.332. Με μια σύνθετη διαβάθμιση:

Και μια σύνθετη διαβάθμιση, τέτοια όπως το φίλτρο συμπαγούς θορύβου, δίνει ένα αποτέλεσμα στροβιλισμού.
Αυτό το φίλτρο προσφέρει τη δυνατότητα κάλυψης ενός μέρους της εικόνας για να την προστατέψει κόντρα στην ενέργεια του φίλτρου.
![[Σημείωση]](images/note.png)
|
Σημείωση |
|---|---|
|
If the image is in indexed mode, this menu entry is disabled. |
Αυτό το φίλτρο βρίσκεται στο κύριο μενού στη σειρά → → . Αυτό το φίλτρο δεν έχει προεπισκόπηση.
Βασικές επιλογές
- Μέγεθος βήματος
-
Το «βήμα» είναι η απόσταση μετατόπισης για κάθε επανάληψη φίλτρου. Μια τιμή 10 είναι απαραίτητη για να πάρετε μετατόπιση ενός εικονοστοιχείου. Αυτή η τιμή μπορεί να είναι αρνητική για αντιστροφή της κατεύθυνσης μετατόπισης.
- Επαναλήψεις
-
Ο αριθμός των επαναλήψεων του αποτελέσματος όταν εφαρμόζεται το φίλτρο.
- Στα άκρα
-
Λόγω της μετατόπισης, ένα μέρος των εικονοστοιχείων οδηγείται πάνω από τα όρια της στρώσης ή της επιλογής και στην αντίθετη πλευρά, οι θέσεις των εικονοστοιχείων αδειάζουν. Οι τέσσερις επόμενες επιλογές επιτρέπουν τη διόρθωση αυτού του θέματος:
- Αναδίπλωση
-
Ότι βγαίνει έξω στη μια πλευρά πηγαίνει στην αντίθετη πλευρά (αυτή είναι η προεπιλογή).
- Μουτζούρωμα
-
Οι άδειες θέσεις γεμίζουν με επέκταση της γειτονικής γραμμής εικόνας.
- Μαύρο
-
Οι άδειες θέσεις γεμίζουν με μαύρο χρώμα.
- Χρώμα προσκηνίου
-
Οι άδειες θέσεις γεμίζουν με το χρώμα προσκηνίου της χρωματικής περιοχής στην εργαλειοθήκη.
- Χάρτης μετατόπισης
-
Για να συμπεριληφθεί σε αυτόν τον επιλογέα αρχείων, ο χάρτης μετατόπισης, που πρέπει να είναι εικόνα σε γκρι κλίμακα, πρέπει να είναι παρών στην οθόνη σας όταν καλείτε αυτό το φίλτρο και πρέπει να έχει το ίδιο μέγεθος όπως η αρχική εικόνα.
Προχωρημένες επιλογές
- Μέγεθος πρόσμειξης
-
Όταν όλα τα εικονοστοιχεία μετατοπιστούν, αυτή η επιλογή τα διασκορπίζει τυχαία, δίνοντας κόκκους στην εικόνα. Όσο πιο μεγάλη αυτή η τιμή (0,00-100,00), τόσο πιο λεπτός ο κόκκος.
- Γωνία περιστροφής
-
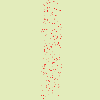
Αυτή η επιλογή ορίζει τη γωνία μετατόπισης των εικονοστοιχείων σύμφωνα με την κατεύθυνση κλίσης της διαβάθμισης. Τα προηγούμενα παραδείγματα δημιουργήθηκαν με μια κάθετη διαβάθμιση και γωνία 90°: έτσι, τα εικονοστοιχεία μετακινήθηκαν οριζόντια και τίποτα δεν έφυγε από τα όρια της εικόνας. Εδώ είναι ένα παράδειγμα με γωνία 10° και 6 επαναλήψεις:
Σχήμα 17.335. Με μια γωνία 10° και 6 επαναλήψεις:
Η μετατόπιση γίνεται σύμφωνα με μια γωνία 10° αντίθετα με την κάθετο. Τα εικονοστοιχεία που φεύγουν έξω από το χαμηλότερο περίγραμμα σε κάθε επανάληψη πηγαίνουν μέσα από το ανώτερο περίγραμμα (η επιλογή αναδίπλωση σημειωμένη), δίνοντας μια διάστικτη γραμμή.
- Υποβήματα
-
Εάν καθορίσετε μια τιμή μεγαλύτερη από 1, το διάνυσμα μετατόπισης υπολογίζεται σε πολλά υποβήματα, δίνοντας σας ένα λεπτότερο έλεγχο στη διαδικασία μετατόπισης.
- Χάρτης μεγέθους
-
In addition to displacement map, you can add a Magnitude map. This map should also be a grayscale image, with the same size as the source image and which must be present on your screen when you call the filter. This map gives more or less strength to the filter on some parts of the image, according to the gray levels of this magnitude map. Image areas corresponding to white parts of this map will undergo all the strength of the filter. Image areas corresponding to black parts of the map will be spared by the filter. Intermediate gray levels will lessen the filter action on corresponding areas of the image. Use magnitude map must be checked for that.
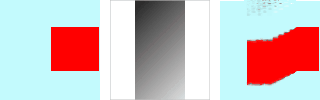
Σχήμα 17.336. Παράδειγμα χάρτη μεγέθους:

Από αριστερά προς τα δεξιά: αρχική εικόνα, χάρτης μετατόπισης, χάρτης μεγέθους μετά την εφαρμογή του φίλτρου «Στρέβλωσης». Μπορείτε να δείτε ότι οι μαύρες περιοχές του χάρτη μεγέθους αποτρέπουν το φίλτρο να επιδράσει.
Πιο προχωρημένες επιλογές
Αυτές οι πρόσθετες επιλογές επιτρέπουν την προσθήκη δύο νέων χαρτών, ενός χάρτη διαβάθμισης και/ή ενός διανυσματικού χάρτη.
![[Σημείωση]](images/note.png)
|
Σημείωση |
|---|---|
|
Για να δοκιμάσετε αυτές τις επιλογές μόνο, πρέπει να χρησιμοποιείσετε ένα χάρτη με συμπαγές χρώμα για όλους τους άλλους χάρτες. |
- Κλίμακα διαβάθμισης
-
Χρησιμοποιώντας ένα χάρτη διαβάθμισης (αυτός ο χάρτης θα πρέπει επίσης να είναι εικόνα γκρι κλίμακας), η μετατόπιση των εικονοστοιχείων εξαρτάται από την κατεύθυνση των μεταβάσεων της γκρι κλίμακας. Η επιλογή Κλίμακα διαβάθμισης επιτρέπει τον ορισμό πόσο οι παραλλαγές της γκρι κλίμακας θα επηρεάσουν τη μετατόπιση των εικονοστοιχείων. Σε κάθε επανάληψη, το φίλτρο δουλεύει σε όλη την εικόνα, όχι μόνο στο κόκκινο αντικείμενο: αυτό εξηγεί τη θαμπάδα.
Σχήμα 17.337. Παράδειγμα κλίμακας διαβάθμισης
Από αριστερά προς τα δεξιά: η αρχική εικόνα, ο χάρτης διαβάθμισης, με εφαρμοσμένο το φίλτρο.
Στο παραπάνω παράδειγμα, το φίλτρο «Στρέβλωσης» εφαρμόστηκε με ένα χάρτη διαβάθμισης (κλίμακα διαβάθμισης = 10,0). Η διαβάθμιση είναι λοξή, από επάνω αριστερά προς κάτω δεξιά. Το μέρος της εικόνας που αντιστοιχεί στη διαβάθμιση μετακινείται λοξά, περιστραμμένο 90° (γωνία περιστροφής 90° στις προχωρημένες επιλογές).
- Διανυσματικό μέγεθος
-
Με αυτό το χάρτη, η μετατόπιση εξαρτάται από τη γωνία που ορίζετε στο πλαίσιο κειμένου γωνία. 0° είναι προς τα πάνω. Οι γωνίες πηγαίνουν αριστερόστροφα. Ο χάρτης ελέγχου διανύσματος καθορίζει κατά πόσα εικονοστοιχεία θα μετακινηθεί η εικόνα σε κάθε επανάληψη.
Σχήμα 17.338. Παράδειγμα διανυσματικού μεγέθους

Από αριστερά προς τα δεξιά: η αρχική εικόνα, ο χάρτης μετατόπισης, με εφαρμοσμένο το φίλτρο.
Στο παραπάνω παράδειγμα, το φίλτρο «Στρέβλωσης» εφαρμόζεται με ένα διανυσματικό μέγεθος. Η διαβάθμιση είναι κάθετη, από πάνω προς τα κάτω. Η γωνία του διανύσματος είναι 45°. Η εικόνα μετακινείται λοξά, 45° προς την επάνω αριστερή γωνία. Η εικόνα θολώνεται επειδή κάθε επανάληψη δουλεύει σε όλη την εικόνα και όχι μόνο στην κόκκινη γραμμή.
- Γωνία
-
Γωνία για σταθερό διανυσματικό χάρτη (δείτε παραπάνω).