This filter displaces pixels of active layer or selection according to the gray levels of a Displacement map. Pixels are displaced according to the gradient slope in the displacement map. Pixels corresponding to solid areas are not displaced; the higher the slope, the higher the displacement.
Figura 17.330. From left to right: original image, displacement map, displaced image

Áreas sólidas na imagem usada como mapa de deslocamento não causam nenhum deslocamento. Um degradê na imagem, que é percebido como um gradiente no sentido matemático: a direção de maior variação das cores, resulta num deslocamento uniforme. A direção de deslocamento é perpendicular a direção do gradiente (ângulo = 90°).
Figura 17.332. Com um gradiente complexo

And a complex gradient, such as the Solid Noise filter can create, gives a swirl effect.
Esse filtro oferece a possibilidade de criar uma máscara para uma parte da imagem, para protege-la da ação do próprio filtro.
![[Nota]](images/note.png)
|
Nota |
|---|---|
|
If the image is in indexed mode, this menu entry is disabled. |
This filter is found in the main menu under → → . This filter has no Preview.
Opções básicas
- Tamanho do passo
-
“Tamanho do passo” é a distância de deslocamento para cada interação do filtro. Um valor de 10 é necessário para resultar num deslocamento de um pixel. Esse valor pode ser negativo para inverter a direção de deslocamento.
- Interações
-
O número de repetições do efeito ao aplicar o filtro.
- Nas bordas
-
Because of displacement, a part of pixels are driven over the borders of layer or selection, and, on the opposite side, pixels places are emptying. The four following options allow you to fix this issue:
- Dar a volta
-
O que sai por um lado aparece de volta na imagem entrando pelo lado oposto (essa é a opção padrão).
- Manchar
-
Emptying places are filled with a spreading of the neighboring image line.
- Preto
-
Lugares que se tornam vazios são preenchidos com a cor preta.
- Cor de frente
-
Lugares que estão ficando vazios são preenchidos com a cor de frente conforme selecionada na caixa de ferramentas.
- Mapa de deslocamento
-
To be listed in this file picker, the displacement map, which should be a grayscale image, must be present on your screen when you call this filter and must have the same size as the original image.
Opções avançadas
- Tamanho da mistura
-
Once all pixels are displaced, this option scatters them randomly, giving grain to the image. The higher this value (0.00-100.00), the thinner the grain.
- Ângulo de rotação
-
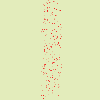
This option sets the displacement angle of pixels according to the slope direction of the gradient. Previous examples have been created with a vertical gradient and a 90° angle: so, pixels were displaced horizontally and nothing went out of the image borders. Here is an example with a 10° angle and 6 iterations:
Figura 17.335. Com um ângulo de 10° e seis interações:
Displacement is made according to a 10° angle against vertical. Pixels going out the lower border on every iteration are going in through the upper border (Wrap option checked), giving a dotted line.
- Subpassos
-
Se você especificar um valor > 1, o vetor de deslocamento é computado em vários sub-passos, resultando em um maior controle do processo de deslocamento.
- Mapa de magnitude
-
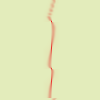
In addition to displacement map, you can add a Magnitude map. This map should also be a grayscale image, with the same size as the source image and which must be present on your screen when you call the filter. This map gives more or less strength to the filter on some parts of the image, according to the gray levels of this magnitude map. Image areas corresponding to white parts of this map will undergo all the strength of the filter. Image areas corresponding to black parts of the map will be spared by the filter. Intermediate gray levels will lessen the filter action on corresponding areas of the image. Use magnitude map must be checked for that.
Figura 17.336. Exemplo de mapa de magnitude:

From left to right: original image, displacement map, magnitude map, after applying “Warp” filter. You can see that the black areas of the magnitude map prevent the filter from taking action.
Mais configurações avançadas
Essas opções extras permitem que você adicione dois outros mapas: um mapa de gradiente e/ou um mapa de vetor.
![[Nota]](images/note.png)
|
Nota |
|---|---|
|
Para testar essas opções sozinhas, é melhor usar uma imagem em cor sólida para todos os outros mapas. |
- Escala de gradiente
-
Using a gradient map, (this map should also be a grayscale image), the displacement of pixels depends on the direction of grayscale transitions. The Gradient scale option lets you set how much the grayscale variations will influence the displacement of pixels. On every iteration, the filter works on the whole image, not only on the red object: this explains blurredness.
Figura 17.337. Exemplo de escala de gradiente
Da esquerda pra direita: Imagem original, mapa de gradiente, filtro aplicado.
In the example above, “Warp” filter is applied with a gradient map (Gradient scale = 10.0). The gradient is oblique, from top left to right bottom. The part of the image corresponding to the gradient is moved obliquely, 90° rotated (Rotation angle 90° in Advanced Options).
- Vector magnitude
-
Com esse mapa, o deslocamento depende do ângulo que você configura na caixa de entrada Ângulo. 0° é para cima. Ângulos aumentam no sentido anti-horário. O mapa de controle de vetor de magnitude determina por quantos pixels a imagem será movida em cada interação.
Figura 17.338. Vector magnitude example

Da esquerda pra direita: imagem original, mapa de deslocamento, filtro aplicado.
In the above example, “Warp” filter is applied with a Vector magnitude. Gradient is vertical, from top to bottom. Vector angle is 45°. The image is moved obliquely, 45° to the top left corner. The image is blurred because every iteration works on the whole image, and not only on the red bar.
- Ângulo
-
Ângulo para o Vetor de magnitude (veja acima).