Fig. 17.43. Exemplul de aplicare pentru filtrul Ascuțire

Imagine originală

Filtrul „Ascuțire” aplicat
Out-of-focus photographs and most digitized images often need a sharpness correction. This is due to the digitizing process that has to divide a color continuum in points with slightly different colors. Elements smaller than the sampling frequency will be averaged into a uniform color. So sharp borders will be rendered a little blurred. The same phenomenon appears when printing color dots on paper.
The Sharpen filter (previously called Unsharp Mask) sharpens edges of the elements without increasing noise or blemish.
![[Indicație]](images/tip.png)
|
Indicație |
|---|---|
|
Some imaging devices like digital cameras or scanners offer to sharpen the created images for you. We strongly recommend you disable this means of sharpening and use GIMP filters instead. This way you regain the full control over the sharpening of your images. |
To prevent color distortion while sharpening, you can Decompose your image to HSV and work only on Value. Go to → → . Make sure the Decompose to Layers box is checked. Choose HSV and click OK. You will get a new gray-level image with three layers, one for Hue, one for Saturation, and one for Value. (Close the original image so you won't get confused). Select the Value layer and apply your sharpening to it. When you are done, with that same layer selected, reverse the process by using Compose. Go to → → . Again choose HSV and click OK. You will get back your original image except that it will have been sharpened in the Value component.
- Presets, „Input Type”, Clipping, Blending Options, Previzualizare, Merge filter, Split view
-
![[Notă]](images/note.png)
Notă Aceste opțiuni sunt descrise în Secțiune 2, „Caracteristici obișnuite”.
- Rază
-
The slider and input boxes (0.0-1500.0) allow you to set how many pixels on either side of an edge will be affected by sharpening. It is better to always sharpen an image at its final resolution.
- Cantitate
-
This slider and input boxes (0.0-300.0) allow you to set the strength of sharpening.
- Prag
-
This slider and input boxes (0.0-1.0) allow you to set the minimum difference in pixel values that indicates an edge where sharpen must be applied. So you can protect areas of smooth tonal transition from sharpening, and avoid creation of blemishes in face, sky or water surface.
Utilizare unei măști neascuțită pentru a ascuți o imagine poate părea destul de ciudat. Aici este explicația:
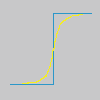
Gândiți-vă la o imagine cu un contrast într-un loc. Curba de intensitate a pixelilor de pe o linie care trece prin acest contrast va arăta o creștere bruscă a intensității: ca o scară dacă contrastul este perfect ascuțit (albastru), ca un S dacă există neclaritate (galben).
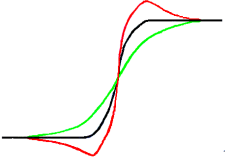
Acum, avem o imagine cu unele zone neclare (curbă neagră) pe care dorim să le ascuțim. Vom aplica mai multă neclaritate: variația de intensitate va fi mai graduală (curbă verde).
Să se scadă intensitatea de neclaritate (curbă verde) din intensitatea imaginii originale (curbă neagră) la intensitatea imaginii originale (curbă neagră). Obținem curba roșie, care este mai abruptă: contrastul și claritatea sunt mărite. QED.
Unsharp mask was first used in silver photography. The photographer first creates a copy of the original negative by contact, on a film, placing a thin glass plate between both; that will produce a blurred copy because of light diffusion. Then both films are placed in a photo enlarger, to reproduce them on paper. The dark areas of the positive blurred film, opposed to the clear areas of the original negative will prevent light to go through and so will be subtracted from the light going through the original film.
În fotografie digitală, cu GIMP, se va trece prin următorii pași:
-
Deschidere imagine și duplicare →
-
In the copy, duplicate the layer → , then from the Filters menu apply → to the duplicated layer with the default IIR option and radius 5.
-
In the Layers dialog of the duplicated image, change Mode to „Subtract”, and in the right-click menu, select „Merge down”.
-
Faceți clic și glisați stratul unic obținut în imaginea originală, unde apare ca un strat nou.
-
Change the Mode in this Layers dialog to „Addition”.
Voila. Plug-inul „Mască neascuțită” face același lucru pentru tine.
La începutul curbei, puteți vedea o adîncitură. Dacă estomparea este importantă, aceasta este foarte profundă; rezultatul scăderii poate fi negativ, iar o dungă de culoare complementară va apărea de-a lungul contrastului, sau un halou negru în jurul unei stele pe fundalul luminos al unei nebuloase (efectul ochiului negru).