Many devices you use in your design or photography workflow, like digital photo cameras, scanners, displays, printers etc., have their own color reproduction characteristics. If those are not taken into account during opening, editing and saving, harmful adjustments can be done to images. With GIMP you can have reliable output for both Web and print.
색상 관리를 하지 않는 이미지 편집의 가장 기본적인 문제는 작업한 대로 보여지지 않는다라는 것입니다. 이러한 것은 두 가지 영역에 걸쳐 나타납니다.
-
카메라, 스캐너, 모니터, 프린터 등 서로 다른 장치의 색상 관리의 차이로 인해 표현되는 색상에 차이가 발생할 수 있습니다.
-
각 장치의 사용가능한 색상공간의 한계 차이에 인해 색상이 달라질 수도 있습니다.
색상 관리의 주 목적은 이미지나 장치에 색상 표현 특성에 관한 설명을 첨부하여, 다음과 같은 문제들을 피하는 것입니다.
이러한 설명을 색상 프로필이라고 부릅니다. 색상 프로필은 장치의 색상 특성을 장치에 독립적인 색상 공간(흔히 작업공간이라고 불리우는)으로 변환하는 테이블입니다. 모든 이미지 편집 작업은 이 작업 공간에서 이루어집니다. 작업 공간에서 장치의 색상 프로필을 이용해 실제로 해당 장치에서 어떻게 보일지 확인해 볼 수도 있습니다.
색상 프로필은 대체로 장치 제작사에서 제공합니다. 이러한 프로필들을 플랫폼이나 운영체제에 관계없이 사용할 수 있도록 ICC (International Color Consortium) 에서는 ICC-프로필 이라는 것을 만들었습니다. 이는 색상 프로필을 파일로 저장하고, 이미지에 내장하는 방법에서 설명할 것입니다.
![[작은 정보]](images/tip.png)
|
작은 정보 |
|---|---|
|
Most of the parameters and profiles described here can be set in the GIMP preferences. Please see 6.4절. “Color Management” for details. |
대부분의 디지털 카메라는 각각의 사진에 색상 프로필을 저장합니다. 그리고 디지털 스캐너는 이 색상 프로필을 가져와 스캔한 이미지에 첨부합니다.
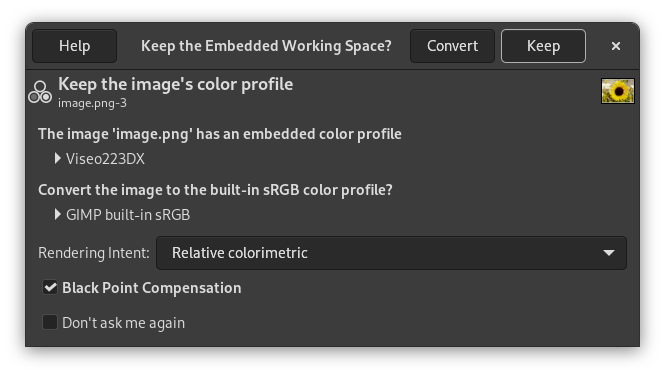
When opening an image with an embedded color profile, GIMP offers to convert the file to the RGB working color space. This is sRGB by default and it is recommended that all work is done in that color space. Should you however decide to keep the embedded color profile, the image will however still be displayed correctly.
이미지에 색상 프로필이 내장되지 않은 경우도 있는데, 이럴 경우 수동으로 색상 프로필을 첨부시킬 수도 있습니다.
For the best results, you need a color profile for your monitor. If a monitor profile is configured, either system-wide or in the Color Management section of the GIMP Preferences dialog, the image colors will be displayed most accurately.
One of the most important GIMP commands to work with color management is described in 5.12절. “Display Filters”.
모니터에 맞는 색상 프로필이 없는 경우에는 하드웨어 측정 도구를 이용해 새로 만들 수 있습니다. 유닉스 시스템에서는 Argyll Color Management System™[ARGYLLCMS] 이나 LProf™[LPROF] 을 이용해 색상 프로필을 생성할 수 있습니다.
For displays there are two steps involved. One is called calibration and the other is called profiling. Also, calibration generally involves two steps. The first involves adjusting external monitor controls such as Contrast, Brightness, Color Temperature, etc, and it is highly dependent on the specific monitor. In addition there are further adjustments that are loaded into the video card memory to bring the monitor as close to a standard state as possible. This information is stored in the monitor profile in the so-called vcgt tag. Probably under Windows XP or Mac OS, the operating system loads this information (LUT) in the video card in the process of starting your computer. Under Linux, at present you have to use an external program such as xcalib or dispwin. (If one just does a simple visual calibration using a web site such as that of Norman Koren, one might only use xgamma to load a gamma value.)
The second step, profiling, derives a set of rules which allow GIMP to translate RGB values in the image file into appropriate colors on the screen. This is also stored in the monitor profile. It doesn't change the RGB values in the image, but it does change which values are sent to the video card (which already contains the vcgt LUT).
Using GIMP, you can easily get a preview of what your image will look like on paper. Given a color profile for your printer, the display can be switched into Soft Proof mode. In such a simulated printout, colors that cannot be reproduced will optionally be marked with neutral gray color, allowing you to correct such mistakes before sending your images to the printer.