![[Note]](images/note.png)
|
Note |
|---|---|
|
For color profile related actions of an image file, see Section 6.8, ““Color Management” Submenu”. For color display related view settings, see Section 5.13, “Color Management”. |
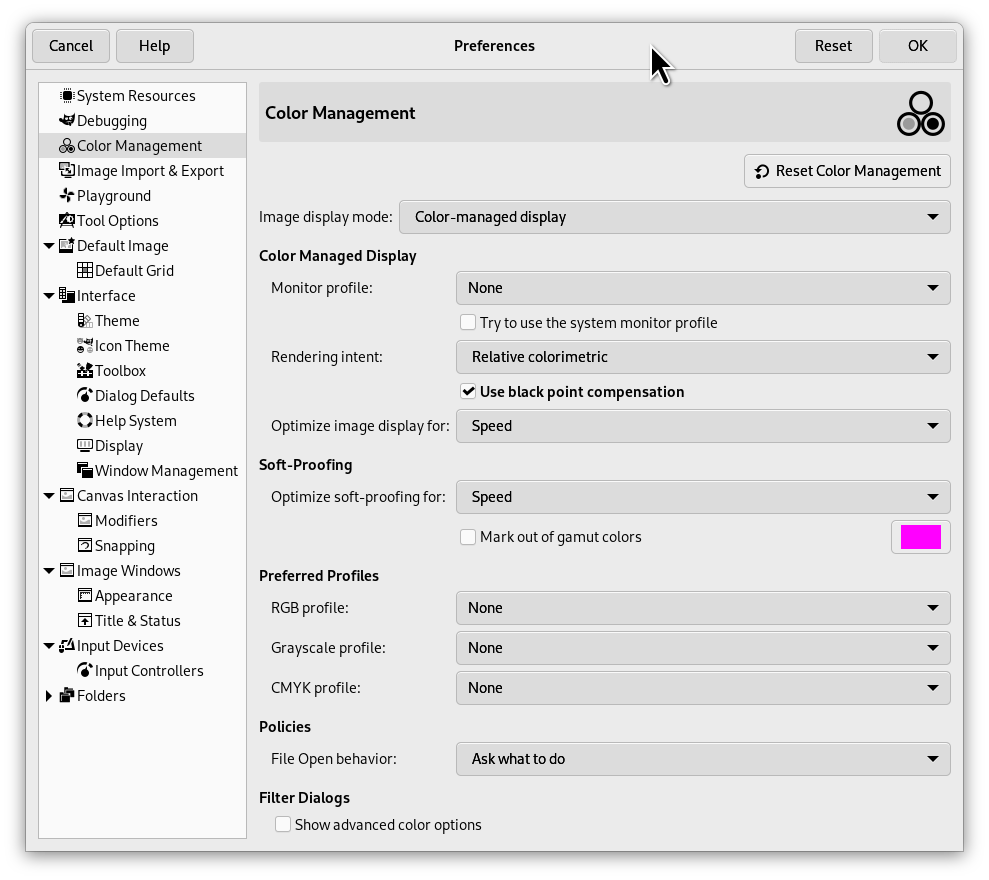
This page lets you customize GIMP color management.
Some of the options let you choose a color profile from a menu. If the desired profile is not present in the menu yet, you can add it by clicking on .
![[Tip]](images/tip.png)
|
Tip |
|---|---|
|
Files containing color profiles are easily recognizable by their
|
- Image display mode
-
Using this option, you can decide how GIMP color management operates. There are three modes you can choose from:
-
No color management: Choosing this disables color management in GIMP completely.
-
Color managed display: This enables GIMP color management and provides a fully corrected display of the images according to the given color profile for the display.
-
Soft-proofing: When choosing this option, you enable GIMP color management not only to apply the profile for the display, but also for the selected printer simulation profile. Doing so, you can preview the color results of a print with that printer.
![[Note]](images/note.png)
Note Please note, that GIMP color management is used to enhance the display of images and the embedding of profiles to image files only. More specifically, the options you choose in this dialog are not used for printing from within GIMP. This is because printing is a special task done by a printing engine that is not part of GIMP.
-
Color Managed Display
- Monitor profile
-
-
None: GIMP uses the colorimetric profile of your monitor.
-
Select color profile from disk: choose a profile that you have available on your computer.
-
Try to use the system monitor profile: When enabled, GIMP will try to use the display color profile supplied by the system. The configured monitor profile is then only used as a fallback.
-
- Rendering intent
-
This option is about how colors are converted from the color space of your image to your display device. Four modes are available: “Perceptual”, “Relative colorimetric”, “Saturation” and “ Absolute colorimetric”.
Relative colorimetric is usually the best choice (default). Unless you use a LUT monitor profile (most monitor profiles are matrix), choosing perceptual intent actually gives you relative colorimetric. See also Rendering Intent .
- Use black point compensation
-
This option is checked by default. Do use black point compensation unless you have a reason not to.
- Optimize image display for
-
Two options: Speed and Precision / Color Fidelity. “Speed” is activated by default. If not, image display might be better at the cost of speed.
Soft-Proofing
Soft-proofing is a mechanism that allows you to see on your screen what printing on paper will look like. More in general, it is soft-proofing from the color space of your image to another color space (printer or other output device).
- Optimize soft-proofing for
-
Two options: Speed and Precision / Color Fidelity. “Speed” is activated by default. If not, soft-proofing might be better at the cost of speed.
- Mark out of gamut colors
-
When this box is checked, the soft-proofing will mark colors that can not be represented in the target color space. On the right there is a color button that you can click to open a color selector to choose the color you want to be used for marking out of gamut colors.
Preferred profiles
- RGB profile
-
Default is “None”, which causes the built-in RGB profile to be used. You can select another RGB working space color profile from disk: it will be offered next to the built-in profile when a color profile can be chosen.
- Grayscale profile
-
Default is “None”, which causes the built-in Grayscale profile to be used. You can select another Grayscale working space color profile from disk: it will be offered next to the built-in profile when a Grayscale profile can be chosen.
- CMYK profile
-
Default is “None”. You can select a CMYK working space color profile from disk to convert RGB to CMYK.
Policies
- File Open Behavior
-
Default is “Ask what to do”. You can also select “Keep embedded profile”, “Convert to built-in sRGB or grayscale profile”, or “Convert to preferred RGB or grayscale profile (defaulting to built-in)” to indicate how to treat embedded color profiles when opening an image file.
![[Note]](images/note.png)
Note For more explanations:
-
ICC Profiles are explained in Wikipedia [WKPD-ICC].
-
See OpenICC project ([OPENICC]) where GIMP and other great names of free infography contribute to.
Some online available color profiles:
-
ICC sRGB Workspace: ICCsRGB™ [ICCsRGB]
-
Adobe RGB98 Workspace: Adobe RGB (1998)™ [AdobeRGB]
-
ECI (European Color Initiative) Profiles: ECI™ [ECI]
-