De opdracht geeft het dialoogvenster “Selectiebewerker” weer. Dit dialoogvenster geeft de actieve selectie in de huidige afbeelding weer en geeft u gemakkelijk toegang tot aan de selectie gerelateerde opdrachten. Het is niet echt bedoeld om direct selecties te bewerken, maar als u werkt aan een selectie, is het handig om alle opdrachten voor de selectie bij de hand te hebben, omdat het gemakkelijker is om op een knop te drukken dan om naar opdrachten te zoeken in de boom met opdrachten of de menubalk. De “Selectiebewerker” biedt ook enkele geavanceerde opties voor de opdracht “Selectie naar pad”.
- De knoppen
-
Het dialoogvenster “Selectiebewerker” heeft verscheidene knoppen voor gemakkelijke toegang tot opdrachten voor selecties:
-
De knop Alles selecteren.
-
De knop Niets selecteren.
-
De knop Selectie omkeren.
-
De knop Opslaan naar kanaal.
-
De knop Selectie naar pad. Als u de Shift-toets ingedrukt houd bij het klikken op deze knop, wordt het dialoogvenster Geavanceerde instellingen weergegeven. Bekijk het volgende gedeelte voor details over deze opties.
-
De knop Selectie belijnen.
-
- Het weergavevenster
-
In het weergavevenster zijn geselecteerde gebieden van de afbeelding wit, niet-geselecteerde gebieden zijn zwart en gedeeltelijk geselecteerde gebieden zijn tinten grijs. Klikken op dit venster werkt als in Selecteren op kleur. Bekijk het voorbeeld hieronder.
Afbeelding 16.20. Voorbeeld van het klikken in het weergavevenster “Selectiebewerker”
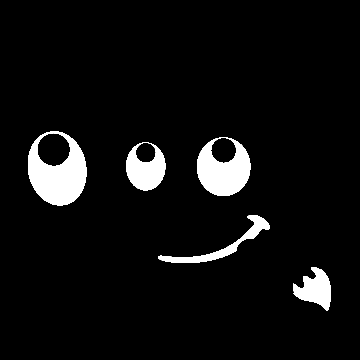
Venster Selectiebewerker na klikken.

Afbeelding met resulterende selectie toegepast.
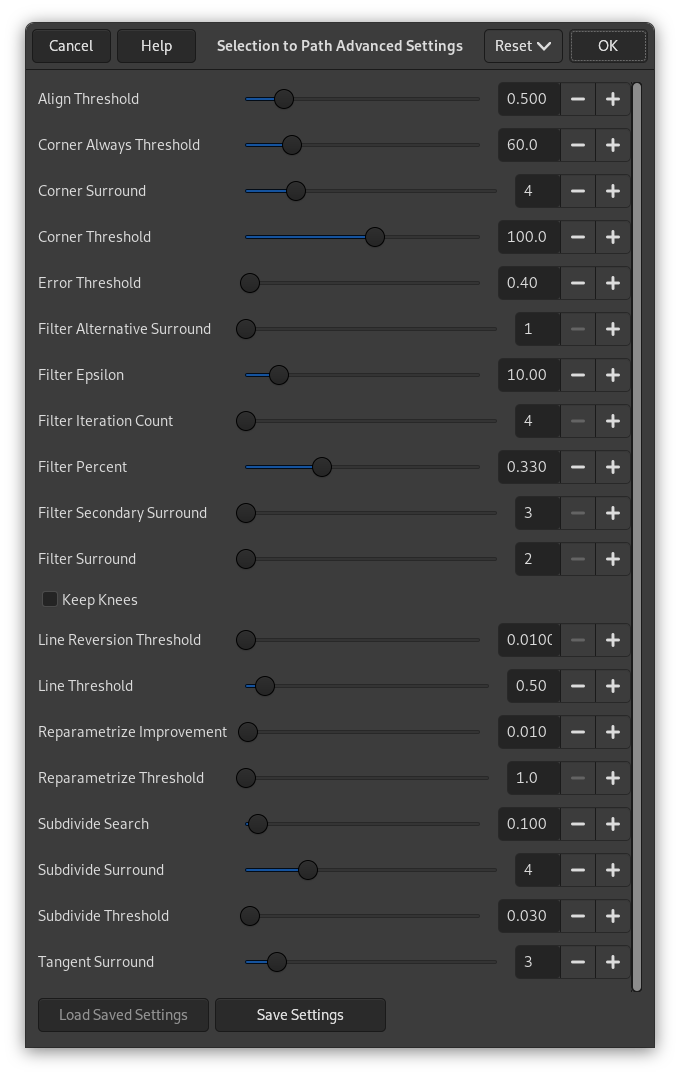
Het dialoogvenster “Geavanceerde instellingen 'Selectie naar pad'”, dat u krijgt door met Shift ingedrukt te klikken op de knop , bevat een aantal opties, de meeste waarvan u kunt instellen met ofwel een schuifbalk of een tekstvak. Er is ook een keuzevak. Deze opties worden meestal gebruikt door gevorderde gebruikers. Zij zijn:
- Align Threshold
-
If two endpoints are closer than this value, they are made to be equal.
- Corner Always Threshold
-
If the angle defined by a point and its predecessors and successors is smaller than this, it is a corner, even if it is within Corner Surround pixels of a point with a smaller angle.
- Corner Surround
-
Number of points to consider when determining if a point is a corner or not.
- Corner Threshold
-
If a point, its predecessors, and its successors define an angle smaller than this, it is a corner.
- Error Threshold
-
Amount of error at which a fitted spline[6] is unacceptable. If any pixel is further away than this from the fitted curve, the algorithm tries again.
- Filter Alternative Surround
-
A second number of adjacent points to consider when filtering.
- Filter Epsilon
-
If the angles between the vectors produced by Filter Surround and Filter Alternative Surround points differ by more than this, use the one from Filter Alternative Surround.
- Filter Iteration Count
-
The number of times to smooth the original data points. Increasing this number dramatically, to 50 or so, can produce vastly better results. But if any points that “should” be corners aren't found, the curve goes wild around that point.
- Filter Percent
-
To produce the new point, use the old point plus this times the neighbors.
- Filter Secondary Surround
-
Number of adjacent points to consider if Filter Surround points defines a straight line.
- Filter Surround
-
Number of adjacent points to consider when filtering.
- Keep Knees
-
This check box says whether or not to remove “knee” points after finding the outline.
- Line Reversion Threshold
-
If a spline is closer to a straight line than this value, it remains a straight line, even if it would otherwise be changed back to a curve. This is weighted by the square of the curve length, to make shorter curves more likely to be reverted.
- Line Threshold
-
How many pixels (on the average) a spline can diverge from the line determined by its endpoints before it is changed to a straight line.
- Reparametrize Improvement
-
If reparameterization doesn't improve the fit by this much percent, the algorithm stops doing it.
- Reparametrize Threshold
-
Amount of error at which it is pointless to reparameterize. This happens, for example, when the algorithm is trying to fit the outline of the outside of an “O” with a single spline. The initial fit is not good enough for the Newton-Raphson iteration to improve it. It may be that it would be better to detect the cases where the algorithm didn't find any corners.
- Subdivide Search
-
Percentage of the curve away from the worst point to look for a better place to subdivide.
- Subdivide Surround
-
Number of points to consider when deciding whether a given point is a better place to subdivide.
- Subdivide Threshold
-
How many pixels a point can diverge from a straight line and still be considered a better place to subdivide.
- Tangent Surround
-
Number of points to look at on either side of a point when computing the approximation to the tangent at that point.